On this page
Pneumonia is one of those medical terms that can send a chill down your spine. It’s a condition we’ve all heard of, but multifocal pneumonia? That sounds even more scary. Don’t worry – we’re here to break it down for you. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into multifocal pneumonia: what it is, what causes it, how it’s treated, and what you can do to prevent it. Let’s get started!
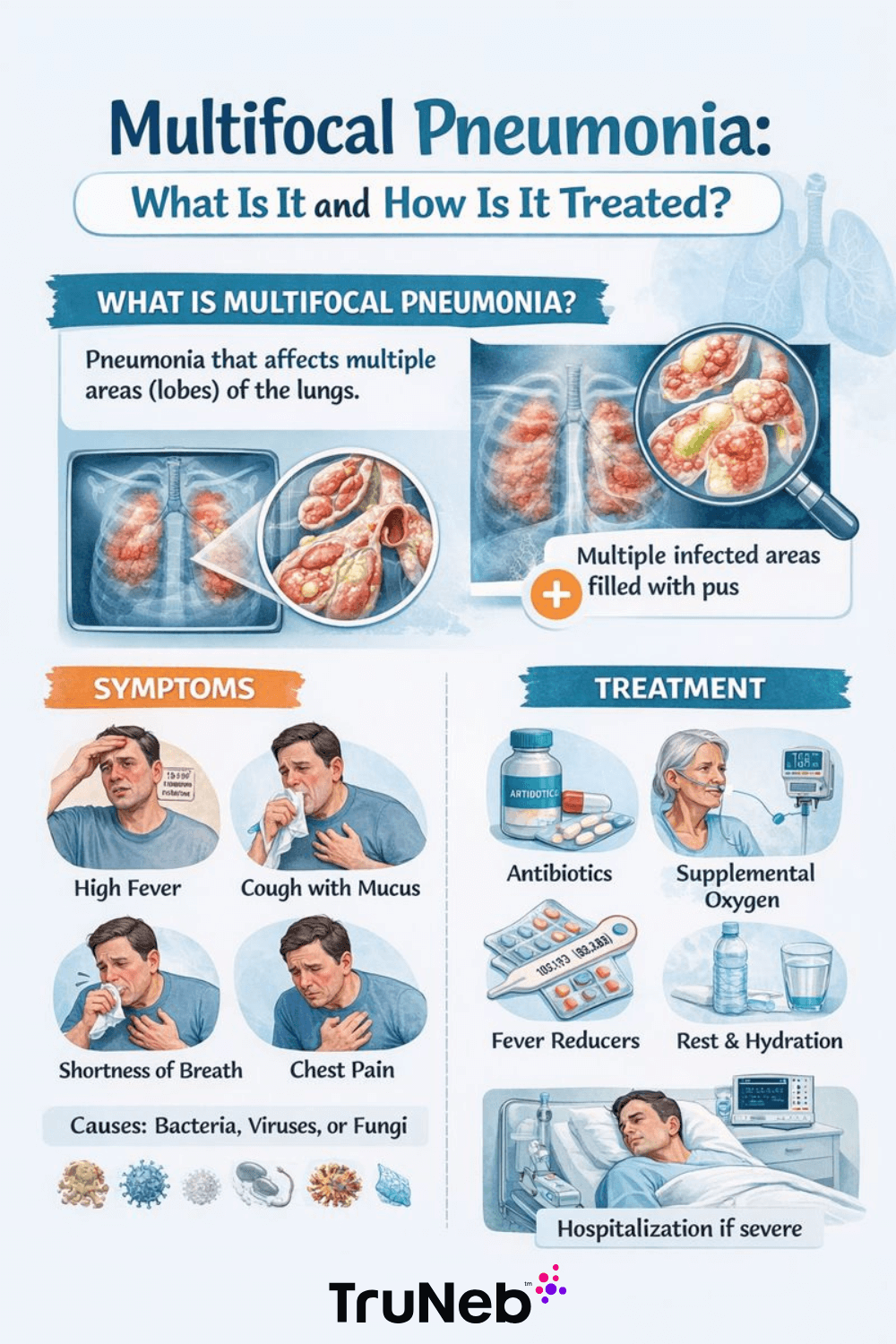
What Is Multifocal Pneumonia?
Imagine your lungs are like a tree, with branches that spread out into tiny air sacs called alveoli. Normally, these air sacs are clear, letting oxygen flow into your bloodstream. With pneumonia, these sacs become inflamed and fill with fluid or pus, making it hard to breathe.
Multifocal pneumonia takes this a step further. Instead of being isolated to one part of the lungs, the infection spreads to multiple areas. Think of it like a storm that’s not content with just one neighborhood – it’s covering the whole city.
The Anatomy of Multifocal Pneumonia
Multifocal pneumonia can:
- Affect one lung (unilateral) or both lungs (bilateral).
- Target different regions or “lobes” of the lungs, which are like compartments.
This type of pneumonia is often more severe because it spreads to multiple areas, potentially causing more damage and making it harder for the lungs to function properly.
What Causes Multifocal Pneumonia?
Multifocal pneumonia can be caused by various pathogens, including:
- Viruses: The usual suspects are respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza, and, more recently, COVID-19.
- Bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae and Legionella pneumophila are common bacterial culprits.
- Fungi: Though less common, fungi like pneumocystis pneumonia or cryptococcus can also cause multifocal pneumonia, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
The type of pathogen matters because it determines the course of treatment. That’s why healthcare providers often run tests to find the cause.
Who’s at Risk?
Multifocal pneumonia doesn’t pick favorites, but certain groups are more vulnerable:
- Older adults (65+)
- Infants and young children
- People with chronic illnesses like COPD or diabetes
- Smokers
- Individuals with weakened immune systems
How Does Multifocal Pneumonia Compare to Other Types?
| Type of Pneumonia | Causes | Symptoms | Severity | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multifocal | Viruses (e.g., COVID-19, RSV), bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae), fungi | Cough, fever, shortness of breath, chest pain, sputum production | Can range from mild to severe; often more severe due to multiple lung regions affected | Antibiotics for bacterial causes, antivirals for viral causes, antifungals, oxygen therapy, nebulizers |
| Lobar | Bacteria (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae), sometimes viruses | High fever, chest pain, productive cough, localized symptoms | Typically severe; may cause lung consolidation in one lobe | Antibiotics, supportive care, oxygen therapy for severe cases |
| Interstitial | Viruses (e.g., influenza), autoimmune diseases, environmental toxins | Dry cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, diffuse chest discomfort | Often mild to moderate but can worsen with complications | Supportive care, corticosteroids for autoimmune causes, oxygen therapy |
| Aspiration | Inhalation of foreign material (e.g., food, liquids, vomit, chemicals) | Cough, chest pain, difficulty breathing, possible cyanosis | Varies; can cause significant respiratory distress if untreated | Antibiotics for secondary infections, suctioning, oxygen therapy, supportive care |
Symptoms of Multifocal Pneumonia
Multifocal pneumonia shares many symptoms with regular pneumonia but can be more severe. Keep an eye out for:
- Persistent cough (with or without mucus)
- Fever and chills
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breaths
- Fatigue or feeling unusually weak
- Rapid breathing or wheezing
In severe cases, you might notice bluish lips (a sign of low oxygen) or confusion, especially in older adults. If you or a loved one experiences these symptoms, seek medical attention promptly.
How Is Multifocal Pneumonia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing multifocal pneumonia involves a mix of detective work and technology. Here’s what healthcare providers typically do:
- Medical History and Exam: They’ll ask about symptoms, recent illnesses, and risk factors.
- Chest X-rays: These can show areas of inflammation or fluid in the lungs.
- Blood Tests: These help detect infection and inflammation.
- Sputum Analysis: A sample of mucus from your lungs can identify the type of pathogen causing the infection.
- CT Scans: In more complex cases, CT scans provide a detailed look at the lungs.
Treatment for Multifocal Pneumonia
The good news? Multifocal pneumonia is treatable. The approach depends on the underlying cause:
Medications
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections.
- Antivirals: For viral causes like influenza or COVID-19.
- Antifungals: For fungal infections.
Supportive Care
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps loosen mucus.
- Oxygen Therapy: For severe cases where breathing is compromised.
- Rest: Allowing the body to recover is essential.
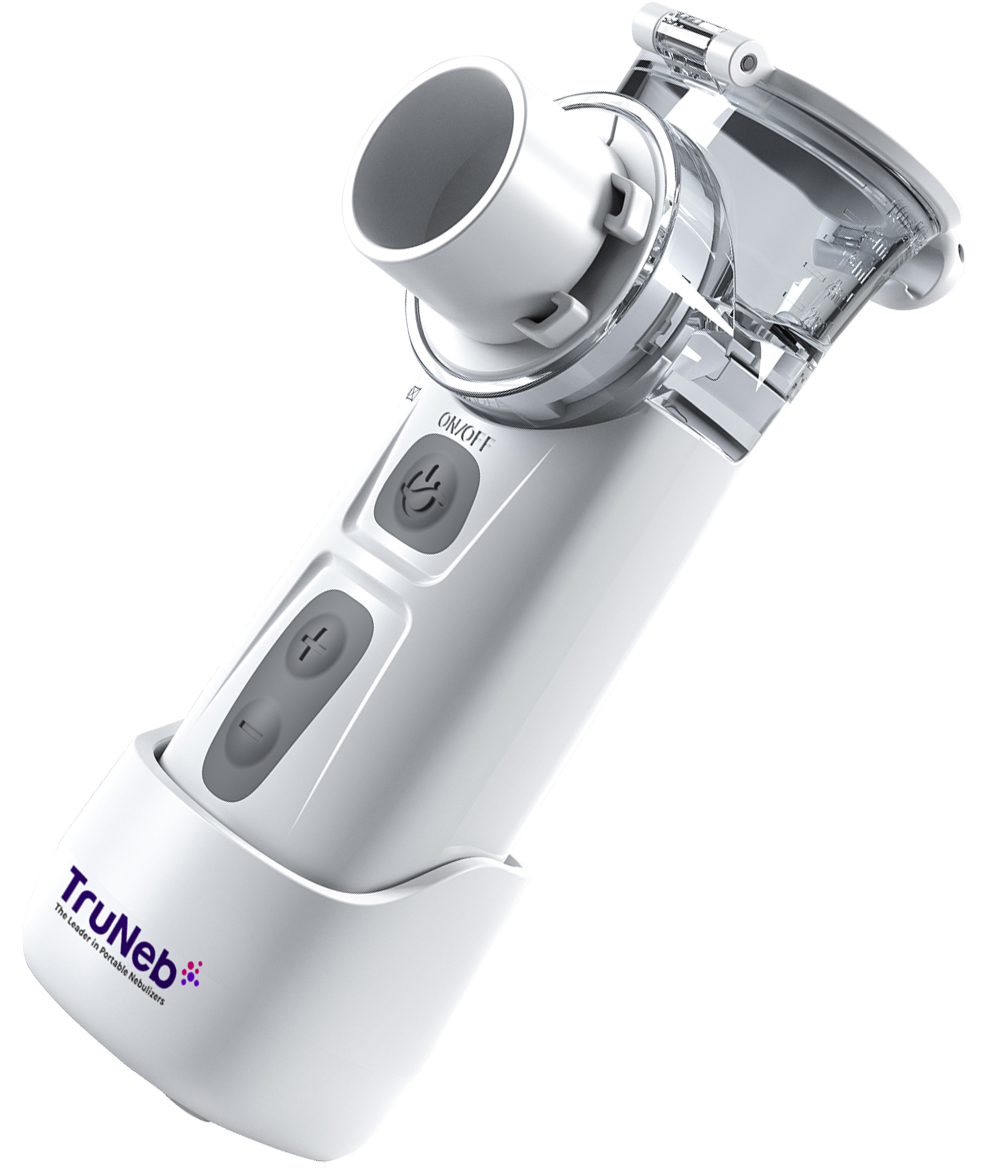
The Role of Portable Nebulizers
For those dealing with breathing difficulties, an inhaler or nebulizer like the TruNeb™ portable saline nebulizer can be a game-changer. They deliver medication like albuterol, steroids, and hypertonic saline directly into the lungs, making it easier to breathe and reducing symptoms. Plus, portable nebulizers are convenient for home use, especially during recovery.
Preventing Multifocal Pneumonia
An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. Here’s how you can reduce your risk:
- Get Vaccinated: Flu shots and pneumococcal vaccines are highly effective.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently and avoid touching your face.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking damages your lungs, making them more susceptible to infection.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise strengthens your immune system.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Keep conditions like diabetes or asthma under control.
Recovery and Outlook
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the infection and your overall health. Most healthy individuals recover within a few weeks, while those with underlying conditions may take longer. Key tips for recovery include:
- Following your doctor’s treatment plan.
- Using a nebulizer to ease breathing.
- Staying hydrated and getting plenty of rest.
Why TruNeb Is Here to Help
Managing respiratory health can be challenging, but tools like the TruNeb Portable Nebulizer make it easier. Designed for convenience and efficiency, TruNeb is perfect for helping you or your loved ones recover from multifocal pneumonia and other respiratory conditions.
Final Thoughts
Multifocal pneumonia may sound intimidating, but understanding the condition and its treatments can go a long way in managing it effectively. Whether it’s recognizing symptoms early, seeking proper care, or using tools like a portable nebulizer, every step helps.
Remember, your health is worth prioritizing. If you suspect multifocal pneumonia, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. And for those recovering at home, TruNeb is here to make breathing a little easier.
*Article reviewed by a licensed Registered Respiratory Therapist
**Last updated 02/08/2026